Which Best Describes the Tertiary Structure of a Protein
The tertiary structure of a protein is dependent on ligand binding A given protein may have separate binding sites for several different ligands Ligands catalyse biological reactions The binding of the ligand results in the inactivation of the protein. Tertiary Structure Definition.
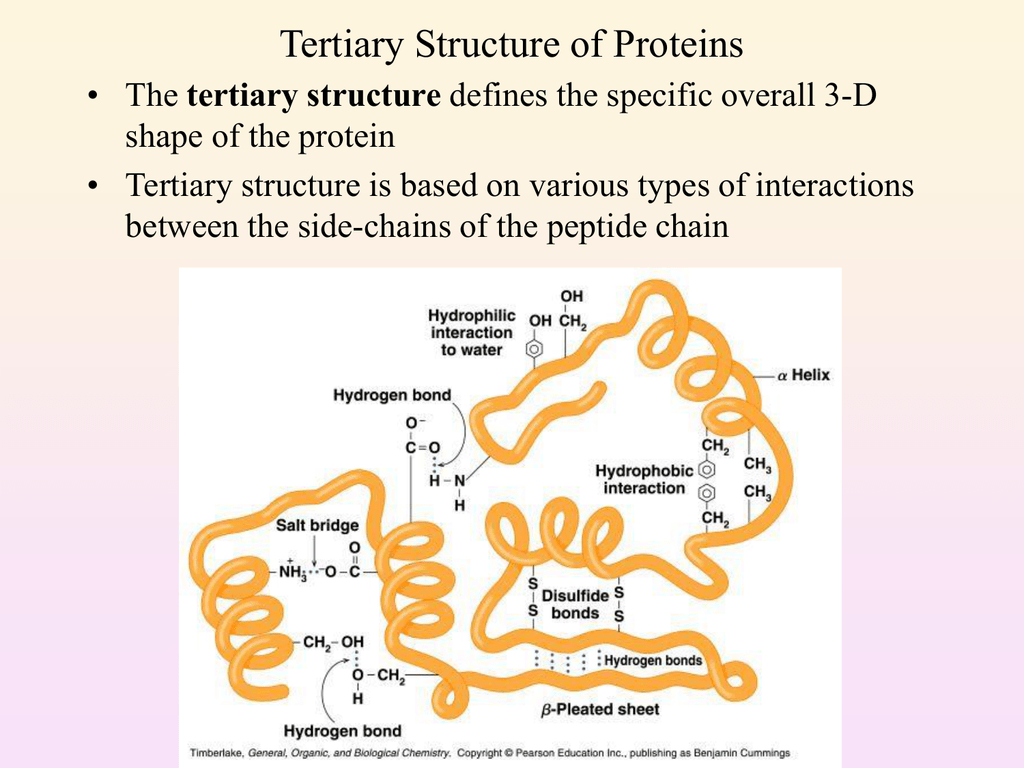
Tertiary Structure Of Proteins
Describe The Tertiary Structure Of Proteins.

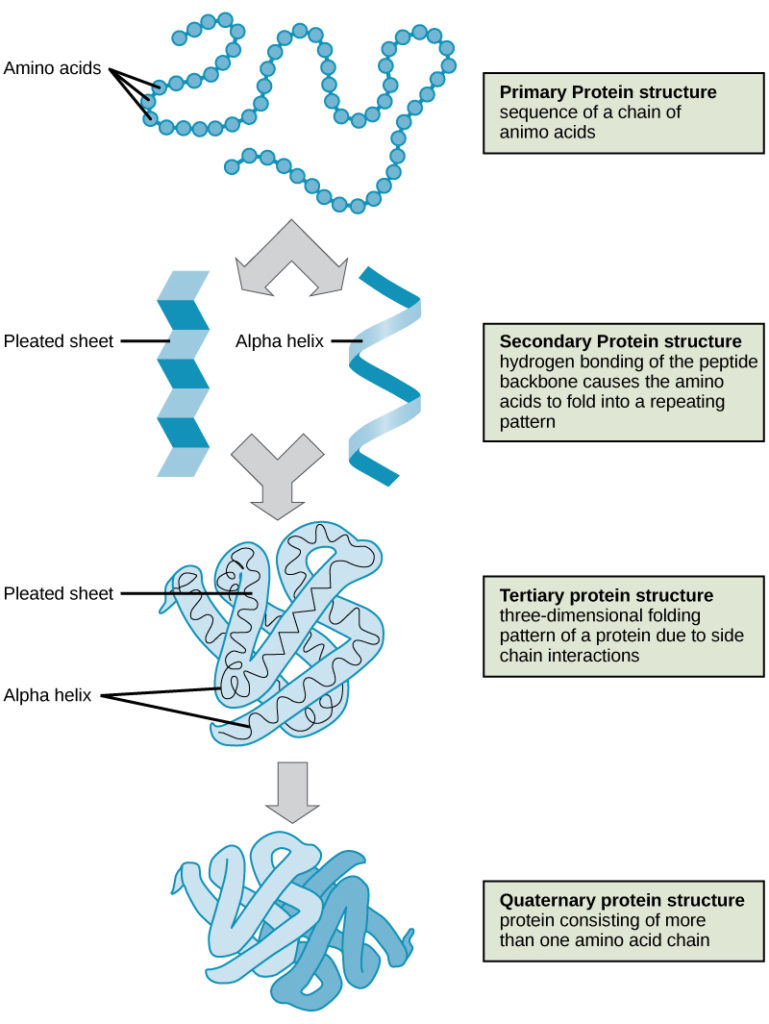
. A single polypeptide chain folded into a three-dimensional shape by ionic polar or covalent bonds. After the amino acids form bonds secondary structure and shapes like helices and sheets the structure can coil or fold at random. The primary structure is a sequence of amino acids linked by peptide bonds bonded through dehydration synthesis.
The polypeptide chains can be homologous or heterologous. The 3-D conformation of a multisubunit protein compose of a number of subunits joined by noncovalent interactions. B-The association of multiple polypeptides.
Of proteins D The ways of protein folding. The polypeptide chain can experience additional foldings to produce the tertiary structure. Quaternary structure of a protein is the way by which two or more polypeptides that make up the protein molecule is arranged.
Which of the following best describes a feature of proteinligand interactions. Which of the following statements best describes the tertiary structure of a protein. To some extent the tertiary structure is determined by the amino acid sequence of the primary structure.
The tertiary structure is the structure at which polypeptide chains become functional. Tertiary structure of a protein describes A The order of amino acids B Location of. The polypeptide chain may undergo coiling and folding to produce the tertiary structure.
A Primary- peptide bonds Secondary- hydrogen bonds Tertiary- disulfide bridges Van der Waals interaction and ionic bonds. Which of these best describes the types of bonds that stabilize each level of protein structure. Summary of Protein Structure.
Primary secondary tertiary and quartenary. The structure formed from interactions between the amino acid side groups. Which of the following statements best describes the tertiary structure of a protein.
You are already familiar with this hierarchy because the most useful starting point for teaching basic protein structure is this structural grouping. Alpha helix and beta pleated sheet. At this level every protein has a specific three-dimensional shape and presents functional groups on its outer surface allowing it to interact with other molecules and giving it its unique function.
Which of the following best describes the tertiary structure of a protein. Which of the following describes the tertiary structure of proteins. A clump of amino acids held together.
Protein structure is stabilized by different types of bonds. This is the structure that gives protein the 3-D shape and formation. These structures are stabilised by the several types of bonds namely hydrogen bond ionic bond van der waals interaction covalent bond disulphide bridges and.
The primary structure constitutes the AMINO ACIDS monomer that makes up the protein. For instance in globular proteins the polypeptide chains are held together in a definite way forming. B Primary- hydrogen bonds Secondary- covalent bonds.
Tertiary Structure refers to the comprehensive 3-D structure of the polypeptide chain of a proteinThere are several types of bonds and forces that hold a protein in its tertiary structure. Central secondary tertiary and quaternary. The Tertiary Structure of a protein is the arrangement of the secondary structures into this final 3-dimensional shape.
Best answer D The ways of protein folding. In which case would a scientist choose to use a dissecting microscope rather than a compound microscope. The structure of proteins includes the primary secondary tertiary and quaternary levels.
Biology 21062019 2130 nnamdi. The proteins function in their tertiary structure controlled by temperature pH. The polypeptides are the subunits that form the protein molecule.
These secondary structure motifs then fold into an overall arrangement. At what level of protein structure would you expect disulfide bonds to be formed between amino acids. Orders of protein structure.
The hydrogen bonds in the secondary and tertiary structure of proteins are directly attacked by. Structurally proteins consists of four levels namely. A linear chain of amino acids held together by covalent bonds.
This is what we call the tertiary structure of proteins. C-The linear sequence of amino acids making up the polypeptide. Which of the following best describes how amino acids affect the tertiary structure of a protein Answers.
Asked Oct 22 2019 in Biology by Shivam01 820k points. A-Characteristic patterns such as helices and sheets that arise when hydrogen bonds form between the amino acids of polypeptides. Hydrophobic interactions greatly contribute to the folding and shaping of a proteinThe R group of the amino acid is either hydrophobic or hydrophilic.
Local regions of polypeptide chains that have a regular conformation which is stabilized by hydrogen bonds. Protein is one of the four major biomolecules in living systems. D-Interactions between different parts.
Linderstrom-Lang 1952 in particular first suggested a hierarchy of protein structure with four levels. 2 Get Other questions on the subject. Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary.
The secondary structure is a helix or pleated sheet mad eof hydrogen bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups. Several polypeptides held together by ionic polar or covalent bonds. The sequence of amino acids in a protein the primary structure will determine where alpha helices and beta sheets the secondary structures will occure.

Tertiary Structure Protein Structure Tutorials Msoe Center For Biomolecular Modeling
No comments for "Which Best Describes the Tertiary Structure of a Protein"
Post a Comment